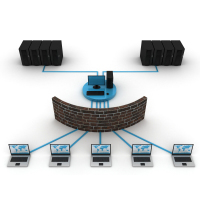
A proxy firewall, otherwise known as a network/proxy server firewall or simply ‘firewall’, is a virtual security appliance that runs on a host computer or server machine and works at the application level. A proxy firewall is a form of packet filtering device, whereby both outgoing and incoming packets (usually in an organization’s intranet) are examined, as well as a “go-between” for users on different networks. A specific set of rules governs which type of packets–based on such items as IP address, source address, destination address–are allowed to enter and exit a private network, such as a LAN or corporate intranet.
Proxy Firewalls Keep Intruders at Bay and Employees In-Check

A proxy firewall typically resides on a single, private IP address that’s distinct from the rest of the hosts on the internal side of the firewall. This masks hosts’ true IP addresses, which are typically very similar and share at least two or three octets (number sets in an IP address: there are four in all).
A distinction should be made between ‘proxy firewall’ and ‘proxy server’. Proxy servers are typically physical machines; one of their functions is act to as a centralized storage machine, whereby multiple users in a small network connect to it and retrieve “cached” copies of files–reducing the load/bandwidth on the network and increasing network efficiency. Proxy servers can also serve as a sort of storage depot for public internet users, especially customers of e-commerce websites.
A proxy firewall, in contrast, is software or an application that primary serves as a security barrier between the outside internet and a private network or internal intranet. Proxy firewalls, however, can and do run on proxy servers. SOCKS must be enabled on both machines tunneling through a proxy, but nearly all modern computers already have this capability.
How it Works
While the specific details go far beyond the scope of this article, the fundamentals of how proxy firewalls operate are pretty simple. A proxy–which is kind of intermediary device in the technological sense–enables clients to establish communicate with other clients (or hosts machines, or servers) without actually making a direct connection. When a user sends a request to another user through a proxy server’s firewall, he/she connects directly to the proxy. The proxy, in turn, requests a connection from the destination address, and the flow of information between hosts is initiated. Through a series of “SYN-ACK” (send/acknowledge) requests, communicate takes place without either host on either side of the firewall ever being connected to one another.
Why communicate like this? Security. As the internet has grown over the last couple of decades, so has the number and amount of people and malicious code circulating. Installing a proxy firewall on a host or server is considered a more basic form of security for organizations, though, and should not be used as a do-all security device. Through layering–adding multiple ‘layers’ of security to a network–network security is hardened.